

It has a very mild flavour and a pleasant crunch. This leafy vegetable also has a lot of water content and helps reduce weight gain.It is considered as one of the best vegetable to eat for people who don’t include enough vegetables in their diet.

Iceberg lettuce has great nutritional values and it acts as a good source of calcium, fiber, iron, potassium, Vitamin A, C& K. This vegetable is enjoyed for its mild favour in varieties of cuisines because of its crunchiness. This vegetable is considered as a wise and economical choice in foods like wraps and sandwiches since it minimizes the risk of spoilage in comparison to other types of lettuce. The leaves of this kind of lettuce has green colour on the outside and the leaves in the center go from pale to yellow colour and almost white as we see the centre of the head. This vegetable has extremely great health benefits. The mature iceberg lettuce leaves grows close to about one foot in diameter. Just like other varieties of lettuce such as romaine and butterhead iceberg lettuce is much sweeter in taste. It has crisp leaves and grows in a spherical head shape. The other word for this cabbage like vegetable is also called Crisphead lettuce. The wedge is your friend.The Iceberg Lettuce has pale green colour leaves and looks quite similar to that of a cabbage. So make some room for iceberg lettuce in your diet by adding it to a salad or on a sandwich. As it turns out, iceberg lettuce is an excellent source of vitamin K, which prevents osteoporosis and heart disease, as well as vitamin A, which is essential for good vision and healthy skin. On a nutrient-density scale of 1 to 100 (100 being the most dense), iceberg lettuce scored 18, trailing close behind broccoli at 34.9 and kale at 49. Surprisingly, iceberg lettuce ranked higher in nutritional value than 18 other fruits and vegetables that are commonly believed to be healthier, such as sweet potatoes, oranges, blackberries, and strawberries. Here’s another kicker: of the 41 items on the nutrient-dense food chart, only seven are fruits. Some of the most nutrient-dense foods included cruciferous items (watercress, Chinese cabbage, collard green, kale, and arugula) and green leafy items (chard, beet green, spinach, chicory, and leaf lettuce) in contrast, items that belonged in the yellow/orange (carrot, tomato, winter squash, and sweet potato), citrus (lemon, orange, lime, and grapefruit), and berry (strawberry and blackberry) groups ranked lower on the list of nutrient-rich foods. After identifying potential PFV, researchers calculated the nutrient density of each item and classified items that provided 10 percent or more daily value of a nutrient as PFV. Since cooking foods can alter their nutrient contents, researchers collected data from only raw foods. To identify potential PFV, researchers consulted scientific literature and consumer guidelines.
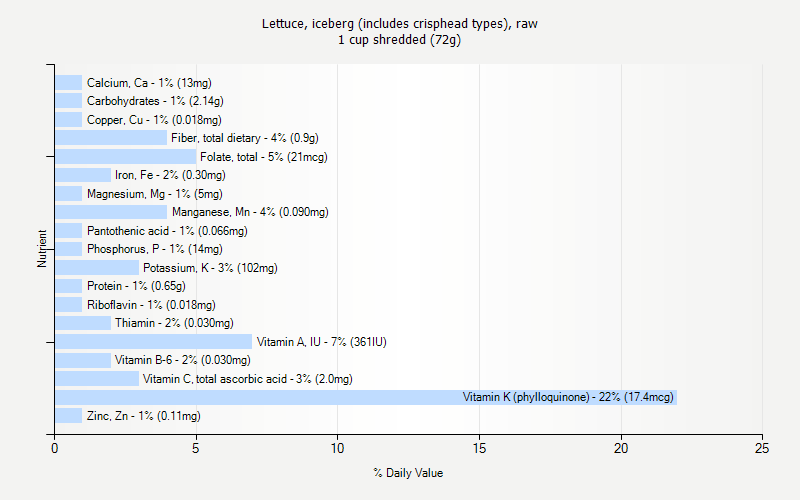
While these foods lack a concrete definition, they can generally be described as “ green leafy, yellow/orange, citrus, and cruciferous items.” According to the researchers, PFV are foods “ providing, on average, 10% or more daily value per 100 kcal of 17 qualifying nutrients.” The nutrients analyzed for each food included potassium, fiber, protein, calcium, iron, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, folate, zinc, and vitamins A, B6, B12, C, D, E, and K, which are considered to be important for public health by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Institute of Medicine. In the study, researchers aimed to find out which powerhouse fruits and vegetables (PFV) could reduce the risk of chronic disease. Iceberg lettuce, a vegetable once thought to have little nutritional value, is now rocking the boat of nutrition and climbing up the chart of nutrient-dense fruits and vegetables. Is iceberg lettuce a food worthy only for rabbits? Not anymore, according to a recent study published by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
